
Search engines do not update their databases instantly. The indexing process might take weeks or even months. That definitely will not be good for SEO. Let us see what exactly the crawl budget is and why you need to optimize it.
What is Crawl Budget
Crawl budget is the number of pages a search engine bot crawls on your website at once. In other words, it shows how many new and updated pages you can provide to a web crawler per its one visit.

This number can slightly change, but it is rather stable. It is important to understand that the limit differs from site to site. An old and popular website gets crawled constantly while any new web-resource is only scanned partially and with delays.
The reason is simple: search engines have limited resources. There will never be enough data centers to instantly track every change on billions of websites around the world. Especially when it comes to unhelpful and unpopular web-resources. When a bot crawls low-quality pages, the crawl budget gets reduced. That will negatively affect your site’s ranking.
Why does it even matter: a web crawler scans a given number of pages at random. You cannot manually make it scan the specific URLs. For instance, your About page might get more hits than a new product category with the newest offers.
Can you affect search engines to improve your crawl budget? Yes, to some extent. We have reviewed the main methods of crawl budget optimization below.
How Does Web Crawling Works
A search engine robot gets the list of URLs on your website to crawl and scans them from time to time. How is this list created? It is generated based on the following elements:
- Internal links on your website, including the navigation tools.
- The sitemap in XML format (sitemap.xml).
- External links.
Robots.txt file tells search engine robots which pages on your website to crawl. Robots check the text file to see whether a specific URL can be crawled. If the URL is not listed in the file, it will be added to the crawling list. Nevertheless, do note that the instructions in the robot.txt file are not obligatory to web crawling bots. It is only a suggestion and recommendation. In some cases, the URL will be indexed anyway. For instance, if links are pointing to it, or redirects to this page in the index, or any other signals that make the search engine spider think that the URL needs to be crawled. As a result, the page will be scanned anyway and Google will send you the warning “Indexed, though blocked by robots.txt”.
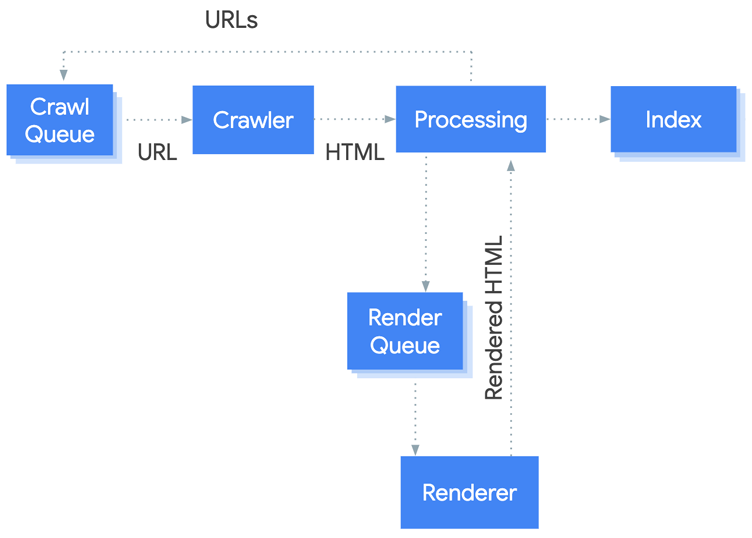
Gary Illyes had explained the crawling process of Google’s bots. Google generates the list of URLs and sorts them by priority. The scanning is performed from the top to the bottom of the list.
How do you identify the priorities? – First of all, Google takes the PageRank of a page into account. Among the other factors are the sitemap, links, and many other things.
As soon as a web crawler scans the URL and analyses its content, it adds new URLs in the list to crawl them (either immediately or later).
There is not a sure way to make a list of reasons why a web crawler bot would scan a URL and why it would not. However, if it decides to scan a page, it will certainly do it. Eventually. When exactly it will do it is partly depends on you.
How to Identify a Crawling Budget Problem?
When a search engine robot finds many links on your site and gives you a large crawl budget, then you will not have any problems. However, what if your site consists of hundreds of thousands of pages but the crawl budget is small? In this case, you will have to wait months for the search engine to notice any changes on your site.
Here are what you can do in order to find out whether you have a crawling budget problem:
- Identify how many pages on your website should be indexed (these pages should not have the NOINDEX meta tag or be listed in the robots.txt file).
- Compare the number of indexed pages with the overall number of pages on your website using Google and Yandex webmaster tools.
- Depending on the web search engine, choose the Crawl Statistics tool or the Crawl Stats report. Google works methodically and usually crawls the site page after page. At the same time, Yandex does not have an explicit system (see the screenshot). Sometimes it does not scan the site at all or only crawls some pages.
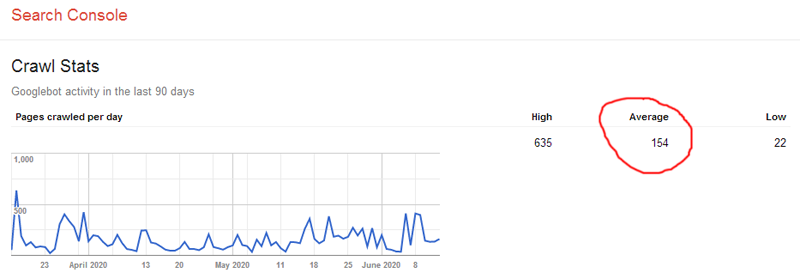
- Divide the number of pages by the average number of the crawled pages throughout a day. If the result is 10 times bigger than the number of pages scanned by a web crawler per day, you will need to optimize the crawl budget. If your number is less than 3, everything is fine.
It is useful to compare the number of pages in the search indexes of Google and Yandex. The workarounds for these systems are different, but the difference should be insignificant. Moreover, the differences in the data set of these webmaster panels will help you get more information and insights.
How to improve the crawl budget
This paragraph includes a lot of points to consider. That is why we will start from the easiest ones up to the most difficult ones. Nevertheless, all of these methods are effective.
The general principle that needs to be learned is that any previously indexed page that a web crawler bot cannot scan several times in a row is removed out of the search index. This applies to the pages that are unavailable for technical reasons (such as 500 errors) and the pages that are blocked from indexing intentionally — for instance, with the NOINDEX tag.
It takes a lot of time for Google to deindex pages. It lasts for a month. Throughout this time, Google conducts periodic checks to see if the page is available. Yandex will deindex a “broken” page faster. However, it will continue to index and deindex it repeatedly until you fix the problems.
Fix the issues
There are only two types of valid server responses for a properly set up website: 200 (OK) and 301 (permanent redirect). Do note that the former should significantly prevail over the latter. All the other responses require careful consideration and fixing, and here is why.
- If you used temporary 302 redirects instead of the permanent 301 redirects for some reason, then the search engine bot will behave accordingly: since the content is temporarily unavailable, the search engine will not delete it. Instead, it will recheck the page periodically. This way you are just wasting your crawl budget.
- The second example is the use of the 404 errors (not found) instead of the 410 errors (gone error). The logic is simple: if the page is removed, the system will try to deindex and forget about it. In case of the 404 error, site crawlers will schedule to recheck the page later.
- 500 errors are the worst. They are a clear sign of a low-quality resource. Because of these errors, the crawl rate limit goes down. As a result, web crawler bots scan your site less and less frequently.
If you see this in your logs or the reports of a SiteAnalyzer, Screaming Frog SEO Spider or their counterparts, find out the reasons and take urgent measures.
Yet another important source of error information is webmaster tools. Use them to monitor the most important pages to receive error notifications and quickly fix them.
Get Rid of Junk Files and Duplicate Content
A search engine’s index should not include service pages, customer pages that duplicate other pages, filter pages, product comparisons, pages with UTM parameters, and draft pages. Stop these pages from indexing using the robots.txt file.

E-commerce websites suffer from duplicate content the most. Duplicate content means that similar content is available at multiple locations (URLs) on the web, and as a result search engines don’t know which URL to show in the search results. Sometimes, Google indexes product pages and even customer sessions, including the products from the cart.
The main rule is to keep only one version of each URL!
Sometimes, it is simply impossible to eliminate duplicate content. In such situations, you can use canonical tags that tell search bots which page should be indexed and what pages should be ignored. In this case, a canonical tag acts like a soft 301 redirect.
Here an example of such a case: a product card falls into two different product categories and is displayed with different URLs. It looks that you have two identical pages with different URLs. Search engines might treat one of these pages as a duplicate of another and index only the master page. However, then they can index both of the pages again. And then remove one of them from the search index. To avoid this and stop wasting crawl budget, use canonical tags if the site content management system does not provide a better solution.
Another possible option is to use the NOINDEX meta tag. Keep in mind, though, that such pages are getting crawled anyway, just less often than usual. Therefore, the crawl budget keeps decreasing. By the way, do not forget to add the Follow attribute to the NOINDEX tag. This way you will prevent such pages from gathering PageRank.
If you want to get rid of duplicate content once and for all, you will have to take more drastic measures than using meta directives for search robots. Consider removing the duplicate content if it is possible.
For instance: you could use variations of the same product that are slightly different from one another (color, size, and other parameters).
Minimize Redirects
The first thing you need to do when performing a technical SEO site audit is to check the home page redirects. It might be available via HTTP or HTTPS, as well as have non-WWW and WWW URLs. These are duplicate versions of the same home page. The search engine might choose any redirect as the master one. You will lose control and waste your crawl budget. That is why you must set up a 301 (permanent) redirect to the correct version.
Besides, you will have to make sure you use only one redirect that is used between the initial URL and the destination URL. Wrong redirection settings might lead to a chain of two or three redirects. This is bad, and here is why. The search robot sees the new URLs and adds them to its list of URLs to crawl. Nevertheless, this does not mean that it will check these URLs immediately. The longer the chain of redirects, the longer the process. As a result, the scanning gets delayed.
Here is a typical example of a bad HTTPS redirect:

The reduced link equity is another problem associated with excessive redirects. Link juice is reduced with each redirection, making your link building less effective.
The home page is not the only place where you should be checking for double redirects. If you have encountered a lot of problems during the pageviews analysis, do not forget to perform a redirect test.
Create an XML Sitemap
The sitemap must include the full list of pages of a website that should be indexed. Important stuff only! Search engines use it as a navigation aid and receive a list of URLs to crawl from it. The sitemal.xml file might include information regarding the creation date, last changed date, importance priority, crawl rate, and more.
Do not be thinking that a web crawler always considers your instructions. You can only hope that the robot will see your list of URLs to crawl and use it eventually. Everything else is usually ignored to avoid manipulation. However, this does not mean that you should not use these directives. Do what you can, but do not expect it to have a 100% effect.
Not every CMS allows you to create a sitemap according to your plans. It might include many unwanted items. What is even worse is that some CMS does not even allow creating sitemaps. In such cases, you can use a third-party plugin or manually submit a sitemap created with software or external service.
Some experts recommend removing all the URLs from the sitemap as soon as the pages get indexed. Do not do this since it might hurt your crawl budget.
Check the sitemap.xml from time to time. The file must not include deleted pages, redirects, and error URLs.
Design a Good Website Structure
This is probably the most difficult step to fulfill. Restructuring a functioning website will not be easy. Creating a proper site structure on the development stage is much easier.
A flat site structure is a website in which all pages are four or fewer clicks away from the home page. Deep site hierarchy has five or more sublevels.
The general principle: deep and complex site structures are more difficult to crawl than the flat ones. Additionally, they are less convenient for visitors. Add ineffective navigation and the lack of mobile optimization, and you will have a full set of SEO issues.
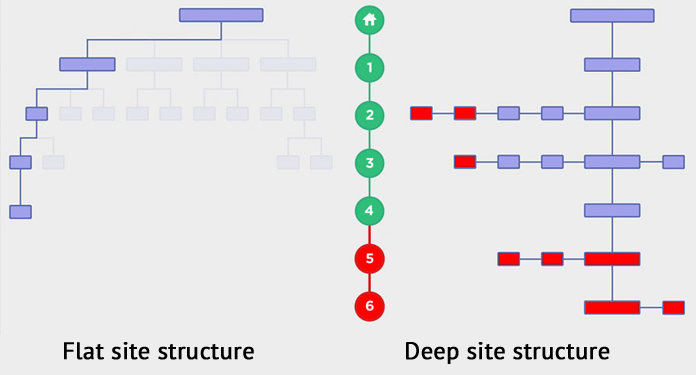
Use the best practices of a flat site structure to make important pages available with very few clicks. Flat, horizontal structure is more preferable than the vertical one.
However, do note that a flat uncategorized structure is not effective either. You need to design a structure that would combine the simplicity and consistency of the hierarchy. Howbeit, this topic requires a separate discussion.
You will need to utilize non-trivial methods that go beyond the technical SEO to optimize your site’s structure. You should start with the visualization of the existing structure. Many website audit tools can help you with that. At this stage, you can start making small adjustments.
If you are planning to make global changes, start from semantics and grouping queries. Identify what can be connected, combined, or moved up a level higher. Probably, you can remove some pages completely.
Do note that Google and Yandex rank sites differently. Your Google rankings will not get high if you have a bunch of spam pages. At the same time, Yandex ranks bigger sites higher even if its content is not top-notch. Therefore, you will have to find a compromise.
Use the Last-Modified header
Most of the website developers and system administrators ignore this important technical parameter. Unfortunately, even some SEO specialists do not understand the importance of the last modified response header.
The Last-Modified header is used to:
- reduce the server load;
- speed up site indexing;
- improve site load speed.
The last modified response header is especially important if your site is big and you update it on a daily basis. However, many webmasters do not use it at all.
How Last-Modified header works
A search robot or browser accesses a specific URL requesting a web page. If it has not changed since the last interaction, the server returns a "304 Not Modified" header. In this case, there is no need to reload content that has been indexed already. However, if there were changes, then the server will send a "200 OK" reply, and the new content will be downloaded.
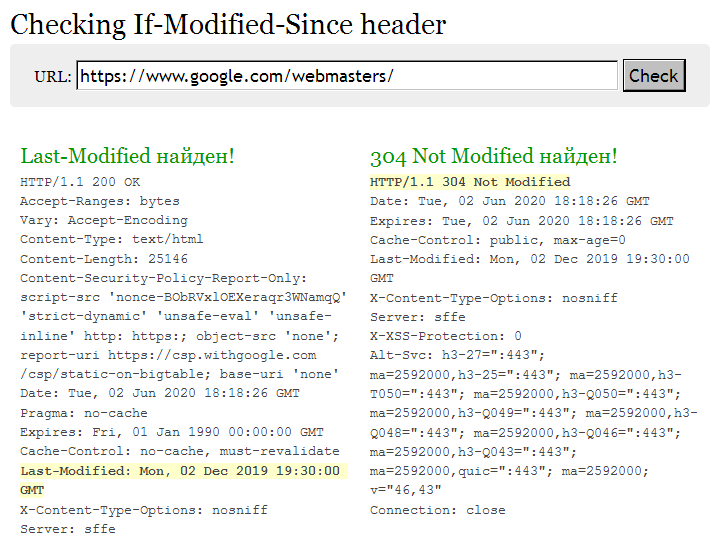
Besides the performance improvements, the search engine updates the date of a page’s content. It is very important in terms of ranking, especially for areas related to human health and finance (YMYL).
Last-Modified allows a crawler to remove some pages from its list that have not been updated. It crawls the updated pages that have been optimized by you. You help to set priorities and save a crawling budget.
Note. Use a Last-Modified header on pages with the most static content. The end-to-end block with the updated content is not what the updated content is and the crawler may not like it. At a minimum, reduce the number of such blocks on the landing pages. What works well on the home page is not required on other landing pages.
You can use HTTP Header Response Checker or similar tools to test this header.
Improve your link profile
If there are a website indexing problems, you should check the link profile. Improving the link profile is the slowest and the most difficult way to optimize the crawl budget, but it is very useful.
Do note that we are not only talking about external links. The internal links speed up indexing too. When a search engine crawler gets a link on a frequently crawled page, a new page will get indexed faster.
The same applies to the link equity, which is transmitted using internal links. The more links lead to a page – the higher its importance for a bot. Distribute the link juice wisely.
Pages linking to themselves, «Hanging Nodes», and Orphan Pages
These mistakes are directly related to the internal linking and cause problems with indexing and crawling. Fortunately, these problems are easy to solve.
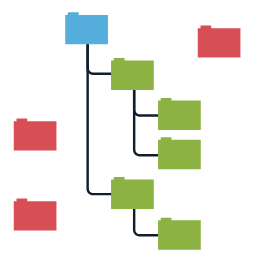
The simplest example of a page linking to itself is a breadcrumb, which indicates where the user is on the site. It does not have to be clickable — you can only use it to navigate visitors. However, you can simply get rid of breadcrumb as well — it will not cause usability issues.
«Hanging node» is a page with no outgoing links. It receives link juice but does not distribute it. It is a dead-end for a search engine crawler that has nowhere to go from the page. Usually, pages like that are not problematic, but you need to analyze it and make adjustments if possible.
Orphan pages pose a much more serious problem. These are pages that are not linked to any other section of the site. Fortunately, such pages are very rare in modern CMS. For instance, the page does not get listed in categories, is not a part of a site’s navigation, or, what is even worse, the site is hacked and the attackers posted their content for external links.
Make crawlers scan your site
You can affect the crawling processes manually. There are several ways to do it.
Re-index pages in webmaster panels. Both Google and Yandex allow you to manually make the crawlers scan changed or new URLs. The biggest disadvantage of the process is a long execution time (up to 10 minutes) in Google and the 20 URLs limit in Yandex.
Make reposts on social networks. Yes, it still works. Choose a social network monitored and scanned by crawlers and leave your link there. Feel free to use your Twitter or VKontakte.
Inspecting logs
Server logs inspection allows you to learn everything about the schedule of web crawlers. However, in some cases, you will not be able to access them. If you have such a problem, you should better change the hosting.
If you do not have server administrator skills, the log will certainly scare you. There is too much data and most of it is useless. If your site is small, you will be able to work with logs even in Notepad ++. However, an attempt to open the log of a large online store might crash your PC. In this case, you should use professional software to sort and filter data.
You can use desktop software such as GamutLogViewer or Screaming Frog Log File Analyzer for data analysis. There are also online services such as splunk.com. Keep in mind that online services are expensive and designed for large amounts of data.
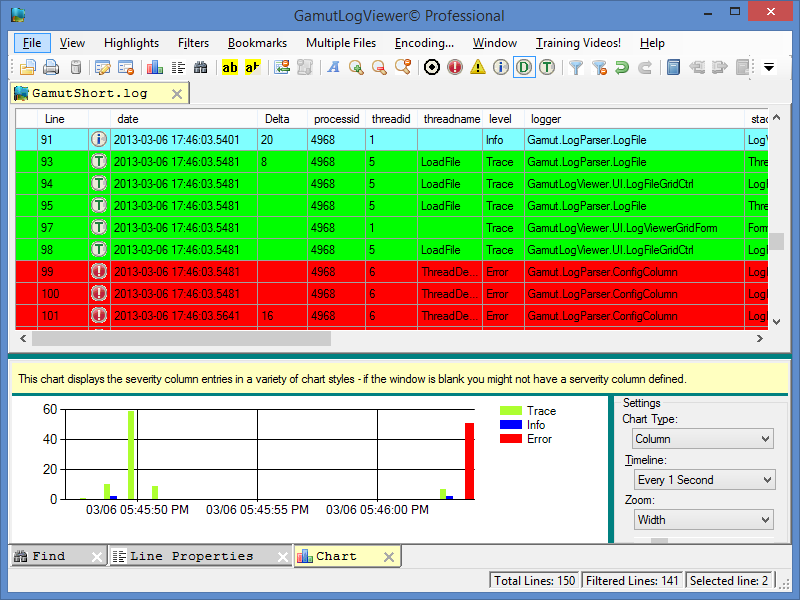
There is a problem: not every GoogleBot you find in logs is actually a GoogleBot. That is why you should check the bot’s IP and use WHOIS to filter out fakes.
Your goal is to process the data for a large enough period (a month is optimal) and find some patterns. You must check the following factors:
- How often the crawler visits your site?
- What URLs are the most visited by crawlers?
- What URLs are ignored by crawlers?
- Has it encountered any website mistakes?
- Does it scan the Sitemap?
- What categories require the most resources?
After you get these data, you will learn if search engine crawlers like your landing pages and why. For instance, you might find that a crawler prefers the informational section of your site. It would be easy to explain: this section of the site has the highest number of internal links
Conclusion
Crawl budget optimization is one of the most important aspects of technical SEO. Overly small crawl rate limit reduces the promoting efficiency. After making the changes, you wait for a change in the ranking. How do you make sure they took measures that have worked even there is no dynamic?
If your site is semantically structured, good from the technical standpoint, and is not very large, then you do not even need to worry about your crawl budget. However, minor improvements will benefit you anyway, so you should devote some time to check your website and implement the necessary changes.
Other articles:




















 6,264
6,264



















