
This post is a symbolic milestone of the past year with thoughts on what affiliate sites for Amazon and other affiliates that we at AdmixGlobal deal with over the past few years should be.
Part 1
The algorithm was updated on November 7, 2019, and although Google says that this is a common regular update, a significant (from 30%) ranking drop of some websites and the growth of others suggests that something significant has happened.
Some webmasters report that their websites have been supplanted by larger and more authoritative resources.
Dmytro Ugnichenko from Megaindex shared his vision in his article "SEO for Low-frequency (LF) Requests Will Not Work Anymore? Google applied the BERT algorithm to all requests".
Here are a few quotes:
- Note. Now the text will be analyzed not in terms of the word occurrence, but by meaning. In other words, the so-called semantic correspondence will now be analyzed.
- The method of website promotion by low-frequency requests may no longer be effective. Reputable websites that do not have optimization for low-frequency requests will have advantage over such websites.
- What should be done? First, reduce the volume of pages on the website. For example, if the website has an iPhone page offering it in different colors, there is no point in creating a page for each color. Such pages should be reduced to a common page. For all URLs excluded from use, either a 301 redirect or the rel=canonical tag should be placed.
If this is the BERT algorithm which is designed to understand the document contents, then, in theory, the Google top should have pages focused on low-frequency requests, but in many cases the exact opposite happened.
A certain confusion also ripens among Amazon affiliates. How to make websites? Will websites focused on low-frequency requests work?
So far, there are no unambiguous conclusions for such well-known specialists as Glen Allsopp as well.
After analyzing 50 dropped websites, in one of the updates of his SEO Blueprint course, he wrote the following:

Glen Allsopp from Gaps.com
The presence of more than a dozen of own and partner websites, where we use different approaches in construction and promotion, as well as monitoring the websites sold helps us to draw certain conclusions.
Over the past month, the guys and I have analyzed more than a hundred "dropped" and "grown" websites.
And if some websites can be attributed problems with links, the use of redirects, PBN, such as bestcarseathub.com, then there are a sufficient number of websites with good content promoted by outreach, where a drop in traffic was an unpleasant surprise for their owners.
One such websites is – coolofthewild.com.
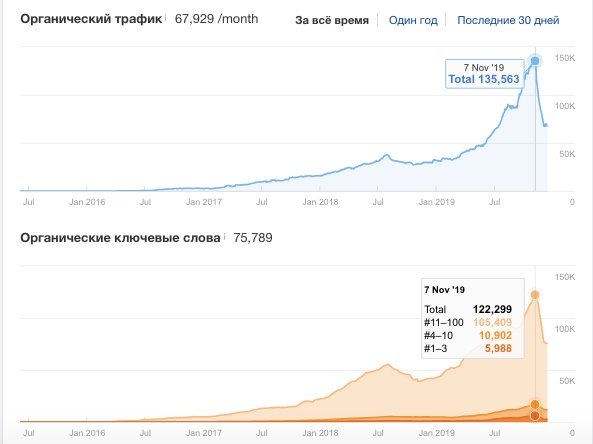
Traffic from coolofthewild steadily grew and dropped abruptly after November 7.
Hundreds of links from reputable resources lead to the website, real authors write there, they have a youtube channel, subscribers on social networks, guys draw infographics, the website contains both commercial content (articles with links to Amazon) and informational articles.
Some webmasters report that low-quality content has also appeared in Google tops.
Indeed, we found enough examples of abandoned projects that have not been updated for many years, with very poor content, but after the update these projects came to life. The screenshot below shows the EMD domain with only 5 articles with affiliate content.
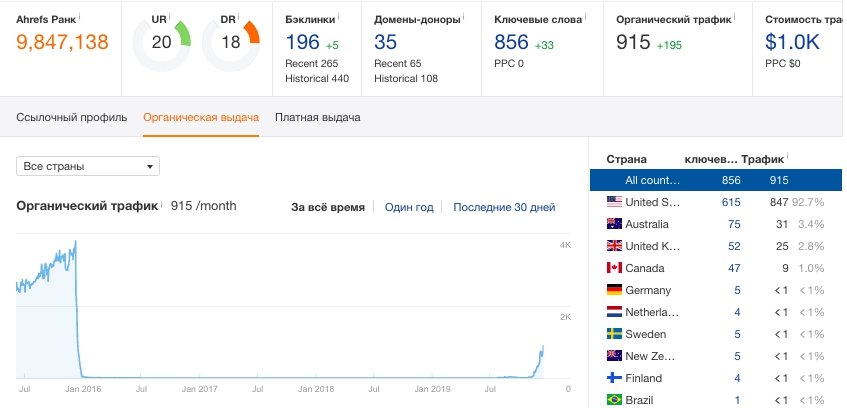
What we managed to find:
- Traffic of dropped websites subsided unevenly, for some pages, growth continued. Although the page is indexed, and you wrote the content yourself, Google may consider your page a rewrite of other sources.
- If you search Google for fragments from your articles requesting individual sentences in quotes, you may find that these separate sentences from your website were copied by doorways, and in some cases search engine ceases to consider your website to be the primary source. Some users write about this as well.
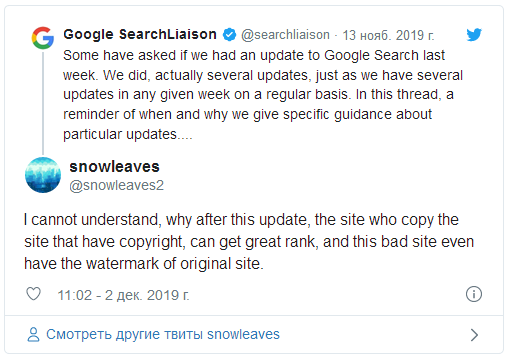
I analyzed the website of one of the subscribers of the AmazonPartnerka Telegram channel and some of the offers from his website fell into "additional results"when searching Google, and the main results included hacked websites and doorways in .tk and .nl domains.
Interestingly, it is useless to submit DMCA complaints through the Google Search Console – such requests are rejected, because the doorway website does not copy a significant part of the text, often this is just one sentence. Also, in many cases, at the time of checking the website by Google moderators, doorway websites were no longer available.
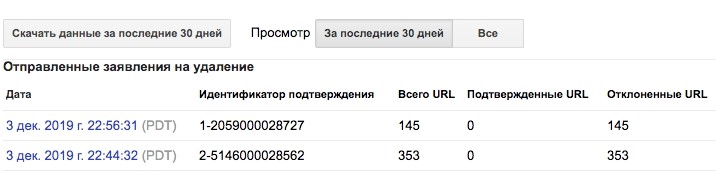
Rejected URLs
We rewrote three articles on several of our websites and traffic returned.
Rewriting the content provided a result to our subscriber as well.
"Hi. It seems to work (rewriting the article)... I rewrote one, re-indexed it, and it immediately got into the top. Traffic resumed... To be honest, I did not think that this was the problem. I thought Google would not allow such a trick. When your content is stolen, and you even suffer because of it...".
The worst part is that you can bring down competitors by stealing their texts to broken (but more trusted in the eyes of Google) websites.
But the rhetorical question remains what to do when your website has 400 pages like coolofthewild.com.
Below are the conclusions:
We came to the conclusion that this was a link-based update and the November ups and downs of websites were not directly related to the BERT algorithm. Changes have occurred in the formula for calculating a link trust.
From now on, a link trust is split between all pages and now the availability of a certain number of links to individual documents is critical. Therefore, for example, multi-page websites running on expired domains, without pumping individual pages with links, will not grow in traffic as well as before, and the doorway page pumped by external links may be "trustier" than yours.
Consider another website that dropped in November. The eco-globe.com project has been launched on an expired domain. The website has 300 pages and after November 7, traffic of the resource has dropped.
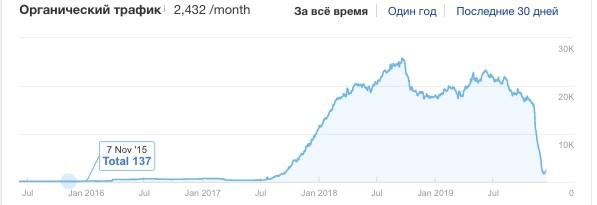
The domain link trust is now clearly not enough for all pages.
One of our subsided websites was outreach-promoted, and those who promoted websites by guest posts know that webmasters prefer not to link to specific landing pages, but to the main page – in section "Author Bio".
As an experiment, we deleted 80 pages from one of our multi-page websites. The result – dropping slowed, and we are now seeing growth for some of the pages. Meanwhile, we did not place external links to these remaining pages.
This does not mean that you should make microwebsites, it means that you should objectively evaluate the available resources in terms of links.
I'll try to draw a simple analogy.
Yes, we all want to plant a large garden (multi-page website), but if you do not have a barrel of water (links) to pour enough water on all green plants, some of them may dry out. If you have a bucket of water, it is better to plant a couple of dozen bushes (pages) so that your plants grow and become stronger.
Part 2
Some experts reacted to my conclusions with a certain degree of skepticism, but let's proceed from the principle that no one knows exactly how Google – works. This is a black box. I do not pretend to be the ultimate truth.

I see, I see ... doorways, bad pagespeed and two h1
At the same time, so far no public expert known to me has given a clear answer to the question why, after the update on November 7, traffic from a number of websites dropped significantly, while others grew, and why before the update some websites grew steadily for 4-6 years, and after that – they subsided.
It is clear that the ranking formula is always a combination of many variables, but what factors have become key in the new version of the algorithm?
Today I will consider a certain example, it will be an affiliate website not from the Amazon niche.
The website was launched on the expired domain, from the first days of May the resource was growing, but on November 7 there was a sharp drawdown in traffic.
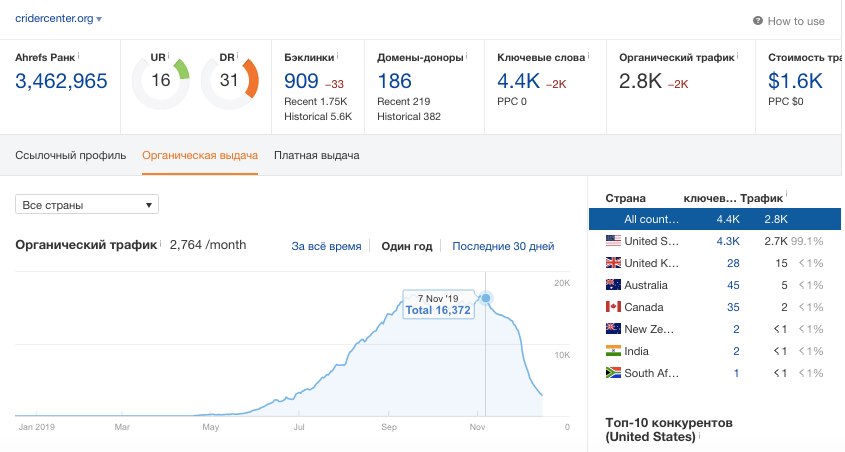
As often happens in such cases, the owner of this website decides that his website is filtered, or does not have enough trust now, buys another expired domain on November 19 and immediately makes a page-by-page redirect to this new domain.
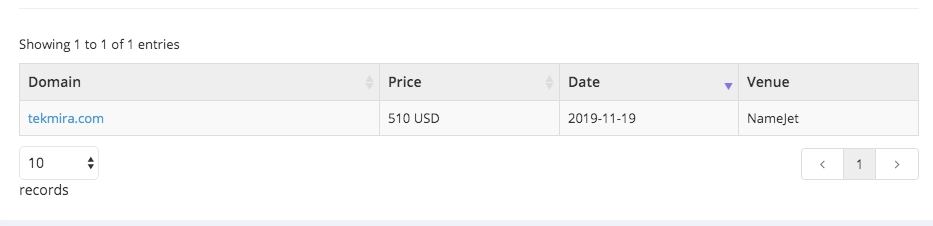
The new expired domain has many good multi-tier links and its own PBNs.
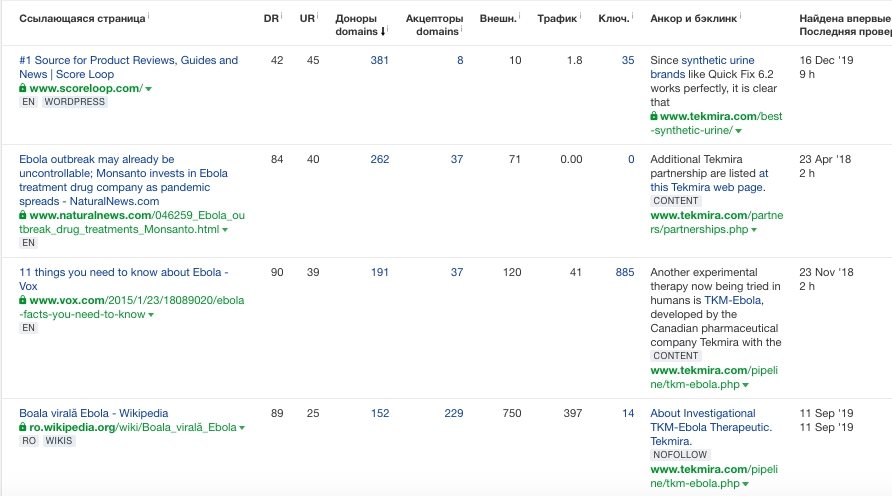
After moving to "more trusted" traffic resumed. And after that...
Stock up on popcorn.
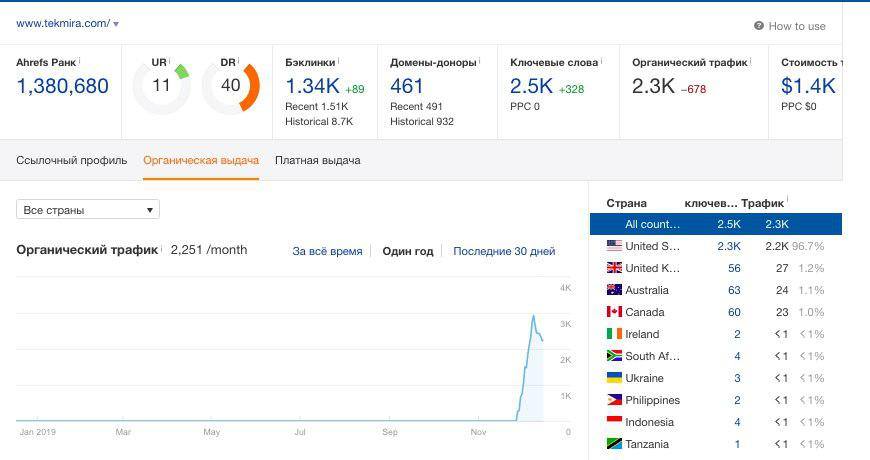
It can be seen that the webmaster is quite experienced, since he does it all very quickly and probably has done it many times.
But, in this case I am confused by the fact that I find doorways by pieces of text from a new domain that uses the texts of the old one.
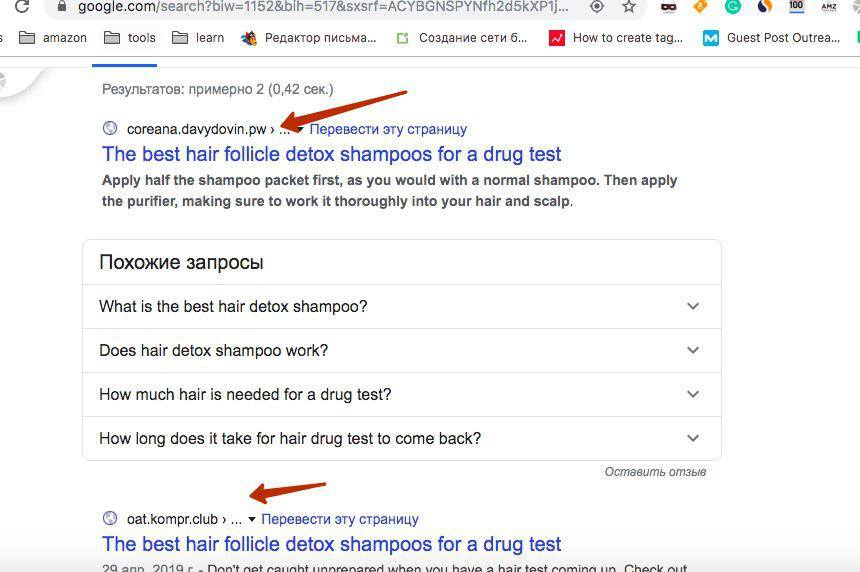
And our new "more trusted" expired domain got into hidden results.
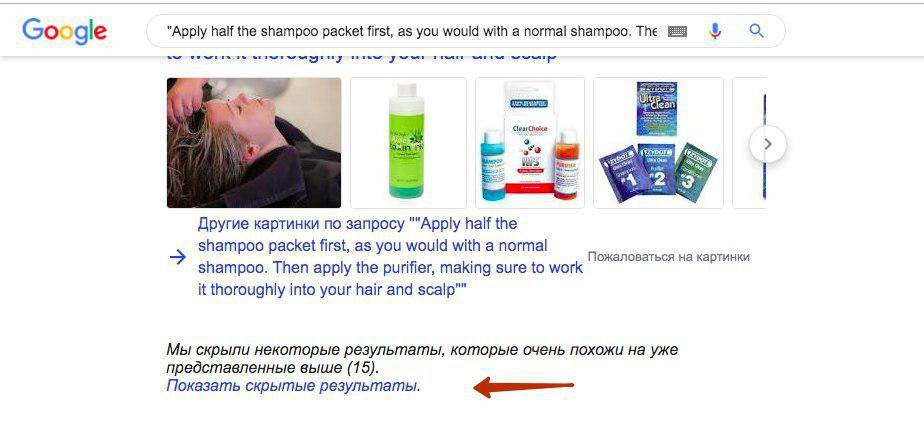
If your websites do not experience such a problem today, this does not mean that it will not occur tomorrow. And, as I already wrote in the first part of the article, it also affected good websites promoted exclusively by white methods.

Come on brother, write fresh articles for my doorways
Thus, a number of questions arise:
- Aren't these doorway websites that copied the texts of the source domain a real cause of traffic drop? And if so, was it possible to solve the problem without moving to a new domain?
- What happened on Google such that in many cases doorways became the primary source?
- How long will this situation last? What should normal websites do?
- How to protect yourself and how to deal with it, because Google does not respond to partial copying of documents in most cases.
- What should multi-page websites do?
I tried to draw conclusions in the previous part, but I will gladly listen to your thoughts in this one.
Written by: Dmitry Sokhach, co-founder at AdmixGlobal
@AmazonPartnerka channel
Other articles:




















 3,511
3,511



















