
Title is a special HTML tag that contains a brief and concise description of the web page content. The <title> tag is placed in the invisible part of the page (in the HEAD block), but you can see its contents on the browser tabs or in the snippet of search engines.
An example of displaying title in browser code:
- <title>How to Correctly Write Title in 2019</title>
An example of displaying title on browser tabs:
In search results:
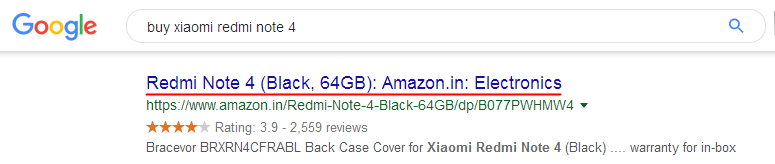
To make a user go from search results to your website, the title tag must be attractive and informative, otherwise the user may choose other, more elaborated snippets of competing websites.
According to the HTML rules, the title tag should be unique for each webpage (not duplicated in different parts of the page code).
Tops for Writing the Title Tag for Google
- Ideally, the tag should contain from 50 to 70 characters with spaces of +-10 characters (as for me, I do not recommend writing title longer than 90 characters).
- Too short titles will be uninformative, and too long ones will dilute the text essence, and the search engine can percieve it as an attempt to manipulate, which may entail sanctions.
- Besides, do not forget that the more words in the title, the less "the weight" of each word (significance from the search engine standpoint), so there is no reason in writing unnecessarily long texts.
- Title should be unique both within one page and within the entire website (ideally, title should be unique within the entire Internet – for this, we add the name of your company / brand to the end).
- In case of diplication of titles of two or more products which, for example, differ in description only in color, weight or size, uniqueness is usually achieved by adding the product identifier in title end in the catalog database (article), or the same parameters that differ by goods. Example:
- Buy black Adidas sneakers, product code XN9730126
- Buy black Adidas sneakers, product code XN9730128
- Buy black Adidas sneakers, size 43
- Buy white Adidas sneakers, size 44
- I do not recommend to make title and h1 the same – it is not mandatory, however there should be at least some minimal difference between them.
- In case of diplication of titles of two or more products which, for example, differ in description only in color, weight or size, uniqueness is usually achieved by adding the product identifier in title end in the catalog database (article), or the same parameters that differ by goods. Example:
- The tag should begin with the most important words and phrases, closer to the end it should include the least important keywords of the page (usually the query importance is determined by its monthly frequency rate in Google Key Planner).
- For example, for product cards, it is advisable to start a title with the words "Buy..., Sell...".
- For regional geo-dependent queries, be sure to include a toponym in the title (city name). This factor will be used both by search engines when ranking, and it will also be useful to visitors for a more rapid understanding of how relevant the page is to their query.
- Example: "Buy a Samsung refrigerator in Paris: prices, sales and delivery of refrigerators - Samsung Paris Office".
- Title should not contain excessive keywords and phrases (so-called "over-spam"). You may not just list all key phrases separated by commas. In the over-spammed form, the text looks unattractive for both search engines and common users. Usually, two or three main key requests are enough to write a correct SEO-optimized title.
- Over-spammed title: "Apartments in New York, buy an apartment in New York, prices for cheap New York apartments".
- Correct title: "Buy inexpensive apartment in New York, prices from USD 50,000".
- Do not use the following when writing titles:
- Excessive unions, prepositions, interjections and particles. You may and should include them in the title text for better readability, but if possible, use them as few times as possible.
- I also do not recommend using superlative adjectives, such as "best, advantageous, big, most", in texts unless they comply with the page content.
- It is not recommended to use punctuation marks ".!?", because they break down semantic passages which reduces the title relevance from the search engines standpoint. Better use ",: -".
- You can use the company name in the title, but in this case, better place it at the end of the text.
- Example: "Buy cheap iPhone in New York from USD 200 - APPLE INC."
- Do not steal titles from competitors – always write your own. The exact title copied from an already indexed page will only harm you, up to the sanctions of search engines. So generate them yourself – be it partially using titles of competitors, but the final text should be unique and should not be the same as the existing options.
- The figures in title work very well, as they attract attention and increase click rate (for example, prices or numerical indication of any features). Example title for an informative article: "10 ways to get acquainted with a girl".
- And the last thing: write title that is readable and attractive to the user – it should hook the user, for example, with its unique offer, so that the user would click on the title and go to the website from the search results.
Note: if the search engine ignores your title and uses other text as the title in the search results, this may indicate a poor-quality title (for example, it is too long, or does not correspond to the page content and does not contain search query). In this case, Google can generate a title from internal link anchors or landing page text (h1-h6 headers, content, anchors).
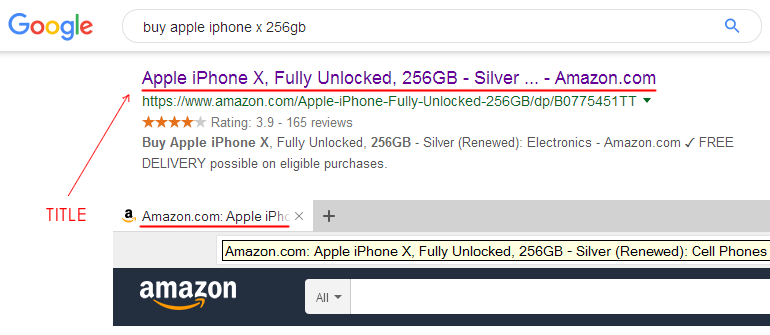
In this example, we see the h1 header in the snippet header, rather than the expected page title.
Title Writing Technology
I suppose you have repeatedly written titles from scratch having at hand only a list of keywords for the page, and I think you will agree that this task is sometimes not easy (you have to" think over "to use most of the keywords from the available list, and on the other hand, ensure that the title text remains readable and does not exceed the maximum length).
However, it is possible to simplify writing titles using ready-made options and "check" them at competing websites from the search engines results.
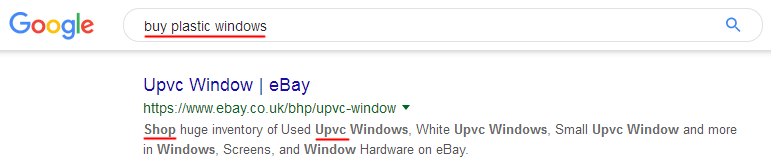
For example, you should write title for the key query "buy plastic windows", as well as for another several similar queries (buy plastic windows in Berlin, buy inexpensive plastic windows, etc.). In this case, we take the first key query "buy plastic windows", enter it in Google and analyze the search results.
During the analysis, we get description options of competitor websites:
- Buy inexpensive plastic windows in Berlin, order PVC windows from EUR 100.
- PVC windows prices in Berlin. Buy windows from the manufacturer.
- Plastic windows inexpensive in Berlin from the manufacturer - buy cheap PVC windows with installation.
- and so on.
As can be seen from the screenshot below, the search engine highlights key words found in descriptions in bold, but often these are not only words from the search query, but also synonyms that the search engine considers relevant and that can be used in title to supplement it and provide it with more semantic proximity to the ideal that the search engine wants to see.
Thus, after such fairly simple manipulations, you can create your own unique title different from competitors and at the same time containing the necessary keywords. I did it like this:
- Buy inexpensive plastic uPVC windows in Berlin from EUR 200
Title Generation for Online Stores

If it is no big deal to write title for websites with a small number of pages (home pages, promotional websites, landing pages), then in case of titles for corporate websites even with a small product catalog, you may experience some difficulties. Writing title manually for product sections and cards of an online store with thousands and tens of thousands of pages is out of question for obvious reasons, since it is both labor-intensive, and most importantly – not effective.
An effective option for writing titles for such websites is their generation based on templates. That is, a certain template applies by programmatic substitution for a huge mass of pages of the same type to generate texts at the output based on certain rules pre-specified by the optimizer.
Pros of title generation:
- you can quickly change content for thousands of pages in minutes
- you can create a large number of templates for most of the options for typical titles of your catalog
- you can experiment with title without spending months of manual labor on it
- no full duplicate pages due to autogeneration
Cons:
- template texts are less readable against "manually written" texts
You can create a template for product cards of your online store or any other catalog using simple rules based on the "available" data from the product descriptions:
- Buy [brand] [model] sneakers in New York for USD [X] in the online store [name_OS]
- Buy an apartment in Paris for EUR [X] thousand, [Y] sq. m, [district], metro [metro_station] - [brand_name]
Results
- Buy Adidas Falcon sneakers in New York for USD 200 in the online store MyBrand.com
- Buy an apartment in Paris for EUR 50,000, 14.9 sq. m, Central District, Saint-Georges Metro - Brand
Title for Service Pages and Not Promoted Pages
Probably, in addition to landing pages, each website contains pages and sections with general information about the website, such as "Contacts", "About", "User Agreement", etc. Although such pages are usually not promoted, they also require titles, but simple and without any frills (search engines judge the website quality not only by the pages promoted, but by the website as a whole, therefore you must write title for all pages).
In this case, title may simply describe a certain page or section. Example for "Contacts" page:
- Contacts - Sony
- Contacts: Sony
- Contacts of Sony
- Contacts: how to get in touch with us - Sony
That is, you come up with a simple description of such pages, i may be brief, the main thing is to be clear and readable.
Emoji in Page Title
Emoji appeared relatively recently, and if earlier we could see them only in messengers and on social networks, now we meet them almost everywhere, and now it is possible to use Emoji for SEO needs as a way to attract attention to the snippet and increase the search engine CTR, and therefore organic traffic.
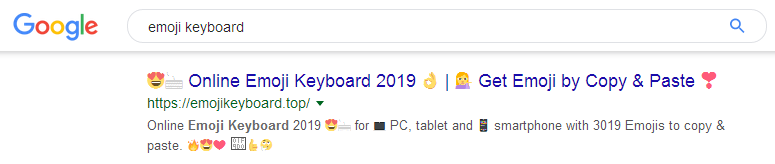
Headlines that use emoji attract more attention than regular text, and also visualize feelings and emotions creating a warmer and friendlier relationship with the audience.
Emoji example: 😎 😄 👆 😍 💋 🌂
You can choose the right emoji here: https://emojio.ru/
Note: At the moment, not all emoji work correctly due to text encodings, so you have to experiment. It is very easy to check emoji – just insert the desired character in Google and click on the search. If the search result headings include these characters, it means that the search engine you have chosen supports them.
Conclusion
With the proper title tag, after several experiments, the SEO specialist can achieve high results in the relevance and clickability of the pages promoted, in a short time and without much effort (keep in mind that a considerable scope of work also falls on the programmer when generating titles).
Important! The page content should correspond to the title, otherwise users will leave the website without finding the answer to their question, and due to an increased bounce rate, the search engine will begin to downgrade the website in search.
You can analyze the TITLE tag optimization of your website absolutely free of charge using the SiteAnalyzer software.
Other articles:




















 8,775
8,775



















